資訊專欄INFORMATION COLUMN

摘要:令人驚訝的是,創作出了一個有一定含義的故事。再次聲明,本文中的示例只為了簡化討論。這是由于精度依賴于初始參數的隨機設定。訓練次數越多超過次精度也會相應提高。
在深度學習中,循環神經網絡(RNN)是一系列善于從序列數據中學習的神經網絡。由于對長期依賴問題的魯棒性,長短期記憶(LSTM)是一類已經有實際應用的循環神經網絡。現在已有大量關于 LSTM 的文章和文獻,其中推薦如下兩篇:
Goodfellow et.al.《深度學習》一書第十章:http://www.deeplearningbook.org/
Chris Olah:理解 LSTM:http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
已存在大量優秀的庫可以幫助你基于 LSTM 構建機器學習應用。在 GitHub 中,谷歌的 TensorFlow 在此文成文時已有超過 50000 次星,表明了其在機器學習從業者中的流行度。
與此形成對比,相對缺乏的似乎是關于如何基于 LSTM 建立易于理解的 TensorFlow 應用的優秀文檔和示例,這也是本文嘗試解決的問題。
假設我們想用一個樣本短故事來訓練 LSTM 預測下一個單詞,伊索寓言:
long ago , the mice had a general council to consider what measures they could take to outwit their common enemy , the cat . some said this , and some said that but at last a young mouse got up and said he had a proposal to make , which he thought would meet the case . you will all agree , said he , that our chief danger consists in the sly and treacherous manner in which the enemy approaches us . now , if we could receive some signal of her approach , we could easily escape from her . i venture , therefore , to propose that a small bell be procured , and attached by a ribbon round the neck of the cat . by this means we should always know when she was about , and could easily retire while she was in the neighbourhood . this proposal met with general applause , until an old mouse got up and said that is all very well , but who is to bell the cat ? the mice looked at one another and nobody spoke . then the old mouse said it is easy to propose impossible remedies .
Listing 1.取自伊索寓言的短故事,其中有 112 個不同的符號。單詞和標點符號都視作符號。
如果我們將文本中的 3 個符號以正確的序列輸入 LSTM,以 1 個標記了的符號作為輸出,最終神經網絡將學會正確地預測下一個符號(Figure1)。
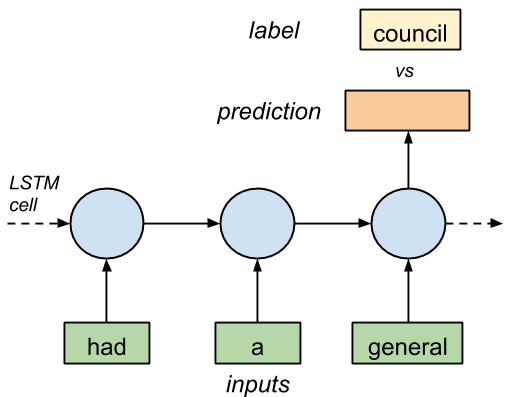
圖 1.有 3 個輸入和 1 個輸出的 LSTM 單元
嚴格說來,LSTM 只能理解輸入的實數。一種將符號轉化為數字的方法是基于每個符號出現的頻率為其分配一個對應的整數。例如,上面的短文中有 112 個不同的符號。如列表 2 所示的函數建立了一個有如下條目 [「,」: 0 ] [「the」: 1 ], …, [「council」: 37 ],…,[「spoke」= 111 ] 的詞典。而為了解碼 LSTM 的輸出,同時也生成了逆序字典。
def build_dataset(words):
? ? count = collections.Counter(words).most_common()
? ? dictionary = dict()
? ? for word, _ in count:
? ? ? ? dictionary[word] = len(dictionary)
? ? reverse_dictionary = dict(zip(dictionary.values(), dictionary.keys()))
? ? return dictionary, reverse_dictionary
Listing 2.建立字典和逆序字典的函數
類似地,預測值也是一個的整數值與逆序字典中預測符號的索引相對應。例如:如果預測值是 37,預測符號便是「council」。
輸出的生成看起來似乎簡單,但實際上 LSTM 為下一個符號生成了一個含有 112 個元素的預測概率向量,并用 softmax() 函數歸一化。有著較高概率值的元素的索引便是逆序字典中預測符號的索引值(例如:一個 one-hot 向量)。圖 2 給出了這個過程。
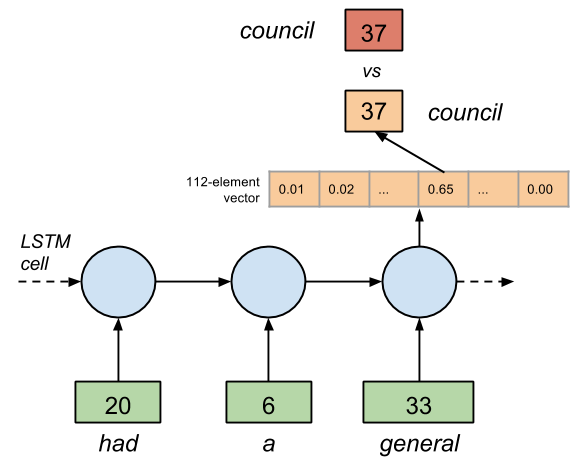
圖 2.每一個輸入符號被分配給它的獨一無二的整數值所替代。輸出是一個表明了預測符號在反向詞典中索引的 one-hot 向量。
LSTM 模型是這個應用的核心部分。令人驚訝的是,它很易于用 TensorFlow 實現:
def RNN(x, weights, biases):
? ? # reshape to [1, n_input]
? ? x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, n_input])
? ? # Generate a n_input-element sequence of inputs
? ? # (eg. [had] [a] [general] -> [20] [6] [33])
? ? x = tf.split(x,n_input,1)
? ? # 1-layer LSTM with n_hidden units.
? ? rnn_cell = rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden)
? ? # generate prediction
? ? outputs, states = rnn.static_rnn(rnn_cell, x, dtype=tf.float32)
? ? # there are n_input outputs but
? ? # we only want the last output
? ? return tf.matmul(outputs[-1], weights["out"]) + biases["out"]
Listing 3.有 512 個 LSTM 單元的網絡模型
最難部分是以正確的格式和順序完成輸入。在這個例子中,LSTM 的輸入是一個有 3 個整數的序列(例如:1x3 的整數向量)
網絡的常量、權值和偏差設置如下:
vocab_size = len(dictionary)
n_input = 3
# number of units in RNN cell
n_hidden = 512
# RNN output node weights and biases
weights = {
? ? "out": tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden, vocab_size]))
}
biases = {
? ? "out": tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([vocab_size]))
}
Listing 4.常量和訓練參數
訓練過程中的每一步,3 個符號都在訓練數據中被檢索。然后 3 個符號轉化為整數以形成輸入向量。
symbols_in_keys = [ [dictionary[ str(training_data[i])]] for i in range(offset, offset+n_input) ]
Listing 5.將符號轉化為整數向量作為輸入
訓練標簽是一個位于 3 個輸入符號之后的 one-hot 向量。
symbols_out_onehot = np.zeros([vocab_size], dtype=float)
symbols_out_onehot[dictionary[str(training_data[offset+n_input])]] = 1.0
Listing 6.單向量作為標簽
在轉化為輸入詞典的格式后,進行如下的優化過程:
_, acc, loss, onehot_pred = session.run([optimizer, accuracy, cost, pred], feed_dict={x: symbols_in_keys, y: symbols_out_onehot})
Listing 7.訓練過程中的優化
精度和損失被累積以監測訓練過程。通常 50,000 次迭代足以達到可接受的精度要求。
...
Iter= 49000, Average Loss= 0.528684, Average Accuracy= 88.50%
["could", "easily", "retire"] - [while] vs [while]
Iter= 50000, Average Loss= 0.415811, Average Accuracy= 91.20%
["this", "means", "we"] - [should] vs [should]
Listing 8.一個訓練間隔的預測和精度數據示例(間隔 1000 步)
代價是標簽和 softmax() 預測之間的交叉熵,它被 RMSProp 以 0.001 的學習率進行優化。在本文示例的情況中,RMSProp 通常比 Adam 和 SGD 表現得更好。
pred = RNN(x, weights, biases)
# Loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y))
optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
Listing 9.損失和優化器
LSTM 的精度可以通過增加層來改善。
rnn_cell = rnn.MultiRNNCell([rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden),rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden)])
Listing 10. 改善的 LSTM
現在,到了有意思的部分。讓我們通過將預測得到的輸出作為輸入中的下一個符號輸入 LSTM 來生成一個故事吧。示例輸入是「had a general」,LSTM 給出了正確的輸出預測「council」。然后「council」作為新的輸入「a general council」的一部分輸入神經網絡得到下一個輸出「to」,如此循環下去。令人驚訝的是,LSTM 創作出了一個有一定含義的故事。
had a general council to consider what measures they could take to outwit their common enemy , the cat . some said this , and some said that but at last a young mouse got
Listing 11.截取了樣本故事生成的故事中的前 32 個預測值
如果我們輸入另一個序列(例如:「mouse」,「mouse」,「mouse」)但并不一定是這個故事中的序列,那么會自動生成另一個故事。
mouse mouse mouse , neighbourhood and could receive a outwit always the neck of the cat . some said this , and some said that but at last a young mouse got up and said
Listing 12.并非來源于示例故事中的輸入序列
示例代碼可以在這里找到:https://github.com/roatienza/Deep-Learning-Experiments/blob/master/Experiments/Tensorflow/RNN/rnn_words.py
示例文本的鏈接在這里:https://github.com/roatienza/Deep-Learning-Experiments/blob/master/Experiments/Tensorflow/RNN/belling_the_cat.txt
小貼士:
1. 用整數值編碼符號容易操作但會丟失單詞的意思。本文中將符號轉化為整數值是用來簡化關于用 TensorFlow 建立 LSTM 應用的討論的。更推薦采用 Word2Vec 將符號編碼為向量。
2. 將輸出表達成單向量是效率較低的方式,尤其當我們有一個現實的單詞量大小時。牛津詞典有超過 170,000 個單詞,而上面的例子中只有 112 個單詞。再次聲明,本文中的示例只為了簡化討論。
3. 這里采用的代碼受到了 Tensorflow-Examples 的啟發:https://github.com/aymericdamien/TensorFlow-Examples/blob/master/examples/3_NeuralNetworks/recurrent_network.py
4. 本文例子中的輸入大小為 3,看一看當采用其它大小的輸入時會發生什么吧(例如:4,5 或更多)。
5. 每次運行代碼都可能生成不同的結果,LSTM 的預測能力也會不同。這是由于精度依賴于初始參數的隨機設定。訓練次數越多(超過 150,000 次)精度也會相應提高。每次運行代碼,建立的詞典也會不同
6. Tensorboard 在調試中,尤其當檢查代碼是否正確地建立了圖時很有用。
7. 試著用另一個故事測試 LSTM,尤其是用另一種語言寫的故事。
原文鏈接:https://medium.com/towards-data-science/lstm-by-example-using-tensorflow-feb0c1968537
歡迎加入本站公開興趣群商業智能與數據分析群
興趣范圍包括各種讓數據產生價值的辦法,實際應用案例分享與討論,分析工具,ETL工具,數據倉庫,數據挖掘工具,報表系統等全方位知識
QQ群:81035754
文章版權歸作者所有,未經允許請勿轉載,若此文章存在違規行為,您可以聯系管理員刪除。
轉載請注明本文地址:http://m.specialneedsforspecialkids.com/yun/4543.html
摘要:首先是最頂層的抽象,這個里面最基礎的就是和,記憶中和的抽象是類似的,將計算結果和偏導結果用一個抽象類來表示了。不過,本身并沒有像其它兩個庫一樣提供,等模型的抽象類,因此往往不會直接使用去寫模型。 本文將從deep learning 相關工具庫的使用者角度來介紹下github上stars數排在前面的幾個庫(tensorflow, keras, torch, theano, skflow, la...
閱讀 3563·2023-04-25 19:56
閱讀 1673·2021-11-12 10:36
閱讀 1789·2021-11-08 13:19
閱讀 1550·2019-08-30 14:06
閱讀 3040·2019-08-30 11:01
閱讀 1736·2019-08-29 13:23
閱讀 2744·2019-08-29 11:18
閱讀 3429·2019-08-26 13:35